Have you recently experienced a massive drop in traffic and rankings?
Has your website been hit by a Google Penguin update, a manual Google penalty, or have you lost lots of traffic and you aren’t sure why? Don’t worry, you aren’t the only website owner that this has happened to and this article will help you to resolve these issues and get your Google penalty removed!
So why have I been targeted?
Have you ever:
1: Hired an SEO company or freelancer to build links to your website?
2: Signed up to a scheme that has guaranteed you first page rankings?
3: Knowingly bought links to improve your page rank?
4: Exchanged links with other websites in return for links to your site?
5: Published excessive amounts of articles containing keyword links to your site?
6: Used automated programs to create links to your website?
7: Created forum comments with keyword anchor text links to your website?
8: Added links to the footer of large amount of websites.
9: Submitted your site to lots of poor quality directories.
10: Bought text links or paid to be included in Blog roll?
If the answer is “YES” to any of the above questions, then you are in breach of Google’s current webmaster guidelines and there is a strong possibility that Google has caught up with you. If the answer is “NO” then contact us today and we will audit your website and link profile for FREE so we can identify the cause of your drop in traffic such as negative SEO.
Many SEO techniques that worked effectively pre-penguin may still give you a short term boost, but if you are in business for the long term, then you must stop using them, clean up your link profile and start new marketing strategies to obtain a more natural looking link profile.
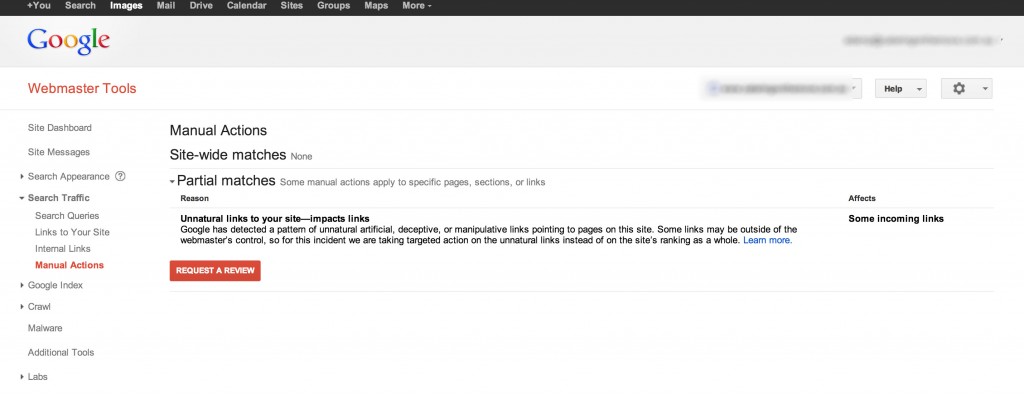
Has your website been manually penalised by Google?
Thankfully Google has made it easy to spot a manual penalty, especially if you have just received a notice from Google saying “we’ve detected that some of your site’s pages may be using techniques outside of Google’s Webmaster Guidelines” or they have updated the “Manual Actions” page in your Google Webmaster Tools account.
If you haven’t received either of the above notifications and you have experienced a serious drop in traffic then this will require further investigation. The first step we would take is to identify when the drop in traffic occurred. Did this happen at the same time as one of the published Google algorithm updates? If it did, this will help us determine the reasons. If it didn’t then we would need to audit your website, look for broken links and other issues that could result in a drop in traffic to your site. For the purpose of this article we are going to assume that you have received a manual penalty or have lost traffic due to a penguin update.
How do you remove a Google penalty?
You have four options:
1: If you retain the monthly services of an SEO agency, ask them what happened?!?!
2: DIY – Read this guide, take the next month or two off work, find all of the problem links and manage them.
3: Hire a team of SEO specialists like High Impact to resolve this issue and generate more traffic.
4: Start again. Launch a new company website on a new clean domain name.
If your current SEO team has been using some old fashioned, (pre-penguin) or spammy link building tactics that have lead to this penalty, then you might want to give them the opportunity to get the penalty removed. I’m sure that they won’t charge you for this work, especially if they caused the problem. Please note, this might not be the quickest solution especially if the agency focus is on paid work.
Unfortunately, everyday your site is penalised; you are missing out on traffic and potentially another sale. Sometimes it’s more cost effective to cut your losses and start working with a new team who have a fresh approach.
Step 1: Collecting inbound link data
The first step is to try and find all of the links pointing to your website. We use a variety of paid and free software tools to crawl the web to find as many links as possible.
There are over a billion websites on the internet, so you can’t expect to find every link. Google can’t even achieve a 100% success rate, despite the resources they have at their disposal. For example, I saw a new link added to Google Webmaster Tools last week for a client’s website that was created in 2008, it was over five years old!
Notwithstanding, Google Webmaster Tools is a great resource, however, it doesn’t publish your full link profile. If you have a penalty, you should use more than one resource to identify the links pointing to your website.
By using as many professional tools as possible we have the best chance of find inbound links, it also demonstrates to Google that you are fully committed to resolve the issue. These are the tools that we use to find inbound links. You won’t find every link pointing to your site, but you should find the majority.
• Google Webmaster Tools – Head over to Google Webmaster Tools, click on ‘Search Traffic’ followed by ‘Links to your site’. Then click more on the ‘who links the most’ tab and download the file. Google is limited to providing only 1000 links, so hopefully we should gather around 20%-30% more links using the other tools.
• Majestic SEO – Is a paid service, but one I would highly recommend. To download the links firstly make sure you click on ‘Use Historic Index’ under the search box. This displays all the data that Majestic has, rather than just the most recent data. Then navigate to the backlink tab and at the bottom of the page click on ‘Download Data’.
• Open Site Explorer – Is another paid service, however, they do offer a free account as well. It is important when using Open Site that you enter the domain name correctly, omitting the ‘www.’ can dramatically change results. Once the page is loaded, click the ‘Linking Domains’ tab and then ‘Export to CSV’. This can take a few minutes but they will email you the report if you so wish.
• Ahrefs – Ahrefs is a really well presented tool, which provides some great information and graphics. To get the backlinks, enter the correct domain and search. On the left hand side you will see the ‘CSV’ tab that downloads the link data for you.
Step 2: Merge and de-duplicate your data
Now we need to organize all of the results. You can export all of the results into a .CSV and use an Excel Spreadsheet or download the data directly to a Google Doc. Create your master spreadsheet using the spreadsheet software that you prefer. One benefit of using a Google Doc, is that you can include a link in your Reconsideration Request when you reach the final stage.
Make sure you have removed all duplicates and then place all the data into your spreadsheet. We create a Master which contains all of the results and then separate tabs for each of the tools that we have used, e.g. Webmaster Tools, Majestic SEO and so on. This helps us manage the flow of data especially when we update results in the future.
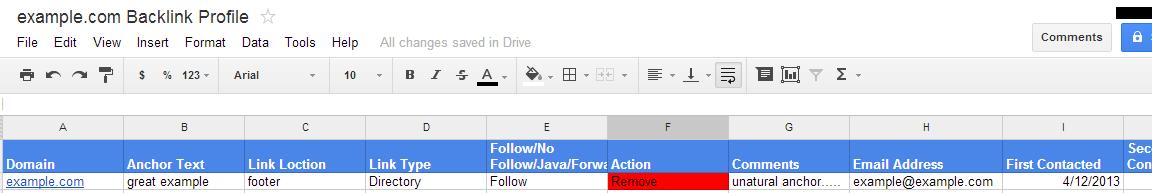
These are the columns that we use when we build a Google Penalty Report for our clients and suggest that you do the same:
• Domain/URL – www.example.com
• Anchor Text – e.g. exact anchor text keyword
• Link Location – e.g. footer
• Link Type – e.g. directory
• Follow/No Follow – e.g. follow
• Action (remove, leave, change) – e.g. remove
• Comments – e.g. gambling website
• Email Address – e.g. webmaster@example.com
• First Contacted – e.g. Date
• Second Contacted – e.g. Date
• Third Contacted – e.g. – Date
• Link Removed Y/N – e.g. Yes, No, requested a removal fee!
This may seem like a lot of work, however, I like to provide our clients with as much relevant information as possible. Sometimes we need to remove a large proportion of links to get a penalty successfully revoked. If a client has previously paid an SEO agency a significant fee to acquire these links, sometimes you need to clearly demonstrate why a link should now be removed.
We have worked with some clients who have previously tried to get a manual penalty removed themselves. One client spent over six months working on this task. They contacted webmasters requesting links be removed, uploaded a disavow list and sent Google many Reconsideration Requests. Their attempts were unsuccessful. Why was this? The main reason was simply because they didn’t identify many of the problem links and they didn’t keep detailed records of their actions. Sometimes you need an SEO expert to identify all of the problem links and keep all the data organised.
It can is difficult for a website owner to give up a link, especially one with high page rank for their most profitable keyword phrase! It cost them time and money to secure this link and in the past would’ve helped with rankings, but this is the old way of thinking! Forget about the past and look to the future. Search engine marketing has changed radically over the last couple of years and now there is a completely new set of rules.
It is always our goal to try and retain as many links as possible for our clients while achieving our ultimate goal, to get the penalty removed. With this is mind, we aim to identify as many links on relevant authority sites that can be updated to meet Google’s webmaster Guidelines.
Step 3: Link Audit
Without a successful link audit you won’t be able to remove your Google penalty. But how should you go about achieving a “successful” link audit and identifying the problem links?
Link audits can be achieved in three ways:
1: Use an off the shelf software solution that claims to identify all “toxic” links.
2: Audit all inbound links yourself.
3: Hire an SEO expert to manually audit all of your links and produce a detailed report.
At High Impact we manually audit all of the URLs with links pointing to our client’s sites. Whilst we do utilise software, we do not rely upon it! To audit a websites inbound links effectively requires specialist knowledge and this process, in my opinion, cannot be completely automated if you want a positive outcome.
We have a huge amount of experience auditing link profiles and this has given us great insight into identifying the links that will have caused a penalty. Spotting a paid link network and other spammy site links has become second nature, which is why we can guarantee our clients a positive outcome.
Here are some examples of what we look for:
• Over Optimised Anchor Text – Links with unnatural anchor text in articles and blogs posts must be removed or changed. For example: There are many ‘great football shops‘ in London where you can buy ‘the best football shirts‘. This is a clear attempt to manipulate rankings and should be removed.
• Low quality directories – Link Directories are very easy to spot and the majority will be low quality and need removing. Many directories have no manual review and accept any links, many have a lot of spammy links pointing to them and the large majority will contain more categories than I thought possible. None of these directories carry any value, and can lead to a penalty, so make sure they are all removed.
• Links in footers and sidebars – Widely distributing links in footers and sidebars on webpages is a recipe for disaster. Do not do it!
• Forum/Blog Comments – Natural comments and blog post are fine and interacting with customers and other companies is great, however inserting optimised links in comments is not.
• Link Exchanges – “Link to me, I’ll link back”…. or links pages simply for the purpose of link exchange need to be removed. It is a direct attempt to manipulate rankings and should not be done.
• Buying or Selling Links – Google actively encourages people to report link selling schemes so avoid them at all costs. They are not natural and will get you punished in the long term.
• Blog Posts – Spammy blog posts can sometimes be hard to spot. Often the URL will be completely irrelevant and the article won’t make sense. Check to see whether the content is duplicated using a duplicate content checker like http://www.plagspotter.com/, or you enter a snippet of text into Google using quotation marks. If the blog is writing about shoes one minute, then web design next, then this can be a tell tale sign of spammy blog. Do the blog posts have over optimised anchor text? If all the posts contain unnatural anchor text then remove the links. Checking the backlinks is probably the easiest way to tell if the blog is spammy. Often these blogs will be part of a link network, or have spammy backlinks.
• Link Networks – A link network is essentially a group of sites that are connected. They will sometimes contain logos claiming to be part of a certain network, however many are harder to find, and you will need to check IP addresses, Google analytic IDs, site design and back links to find out whether it is a link network.
• Widget Links – Widgets are not a bad thing in themselves, though including an embedded link back to your site in them is.
Once we have completed the link audit and identified all of the bad links, we are ready to start working on getting them removed.
Step 4: Removing bad links
Once you have identified the problem links, you will need to get as many removed as possible. To do this you will need to contact all of the website owners or webmasters and send them a “link removal request”. Before you can do this, you will need to find their contact details or use a contact form if they have one published on the website.
Finding contact details can sometimes be challenging if they aren’t published on the websites “contact us” page. If this is the case then you will need to start doing a little bit of investigative work. We use “who is” look up services like Domain Tools to help us find who a domain name is registered to and hopefully their contact details. If this fails, you will need to try and find their Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter or Google+ and use social media to make contact. Finally, if they don’t have social media, you can always Google the domain name and see what results appear, it may return contact details.
You won’t find all of the contact details, but it’s worth investing time to try and find as many as possible because getting links removed is better than just disavowing them.
Step 5: Contacting Webmasters
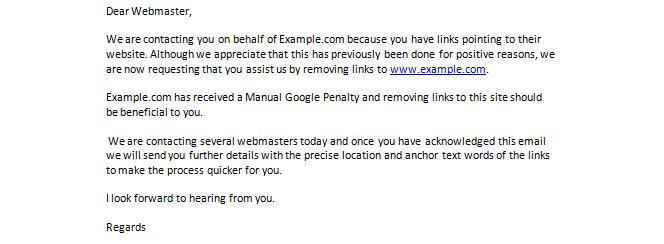
Contacting the webmasters is an important part of the link removal campaign and writing a polite and concise email is essential to get bad links removed.
When writing your email template to webmasters, use these tips to help you:
• Be polite. Remember they are assisting you by removing a link, which will take up their time. There is no need to make threats about reporting them to Google.
• Be concise. Do not bog your email down with too much unnecessary information, they just aren’t going to read it and it’s wasting more of their time.
• Don’t send multiple emails without giving them a chance to respond; many directories for example, will be getting a large number of emails to remove links so it may take a few days for them to respond. We typically send up to three emails over a two week period.
• For the first email, I would recommend sending a broad e-mail and then following up a response with specifics. When they get back to you, you can provide a list of the offending links that you would like to have removed, list the pages that they are on and generally make it as easy as possible for the Webmaster to complete the task.
Once you have given a reasonable amount of time for the webmasters to respond. It is time to start contacting those who didn’t get back to you. Make sure that you do not email any webmasters that have already got back to you by keeping your spreadsheet well organised and up to date.
All of your emails should be polite and professional. However, for the second and third emails, let the webmasters know that it’s in their interest to remove your link. For example, you could include a sentence saying something like this, ‘by removing our link from your website could be beneficial to you because it will avoid us from having to include your website on a disavow list, which may alert Google to your website”. This has helped increase our response rate.
Some webmasters will respond favourably, some will ignore you, and others, will request an admin fee for removing a link. I appreciate that time is money and if the fee is reasonable, then you may wish to pay it. These requests typically range from $2 up to $25. The most we have been asked for to date is a very unreasonable £250…from a Director of a UK based SEO agency. However tempting, we won’t name and shame him.
Step 6: The Disavow Tool
If you haven’t been able to remove all of the problem links, which is very likely then you will need to use the disavow tool. Google recommends that you try to remove as many spammy or low quality links as possible before using this tool, so I would advise not to skip the manual removal unless you want to receive a failed reconsideration request.
Matt Cutts, the Head of the Google Spam team explains when you should use the disavowal tool in this video:
How to create a Disavow file
To create the disavow file you will need to use Notepad or a plain text file.
To remove all links from a particlular domain enter:
domain:exampleurl.com
Otherwise just include the urls of the offending links:
http://example.com/offendinglink/
You can also use the ‘ # ‘ character to include additional information about excluded links and make sure that there is only one domain per line.
When you have finished collating all the data you need to save the file as a .txt and it must be encoded in UTF -8 or 7 -bit ASCII.
Uploading a new file will replace any previously uploaded ones, so make sure that if you have already uploaded a file to include those links in the new list. Once this has been completed head to the disavow links page, select the correct domain and upload the list.
Step 7: Sending the Reconsideration Request
The reconsideration request is hopefully the last piece of the puzzle. What you write and the information that you include can make the difference between success and failure. You aren’t writing a letter, so don’t get emotional and include phrases like “we are losing sales as a result of this penalty”, focus on the causes of the penalty and what you have done to resolve the issue.
In the request you need to include the following information:
• What you were doing wrong and how you have now rectified the situation. If you were using an “SEO Company” state that, and say that you are no longer working with them, and that you are now using tactics that adhere to the webmaster guidelines.
• What you have done to fix the problems that were causing the penalty. Make sure that you include a link to the Google Doc showing all your hard work and explain that all webmasters were contacted three times in an attempt to remove the problem links.
• Lastly, be polite and apologise for causing the problem in the first place. This is not Google’s fault. They are trying to provide the user with the best possible experience and artificially attempting to manipulate the rankings is wrong.
Sit back and relax…?
I have read many articles claiming now is the time to sit back and wait, however, in our experience there is still work to do!
Google indexes new websites and links every day. Remember the link we mentioned previously from 2008 that was added to Webmaster tools in late 2013…this happened to be added after we had sent a reconsideration request and while we were waiting for a response. Because of this link, the request failed. When we included it in our second attempt, the penalty was successfully removed!
Since then, we have had instances of 20-30 new linking URL’s appearing in Webmaster tools in a couple of days after we have uploaded as disavow and sent a reconsideration request. To manage this, we quickly audit the new links and update the disavow file with any additional problem URL’s.
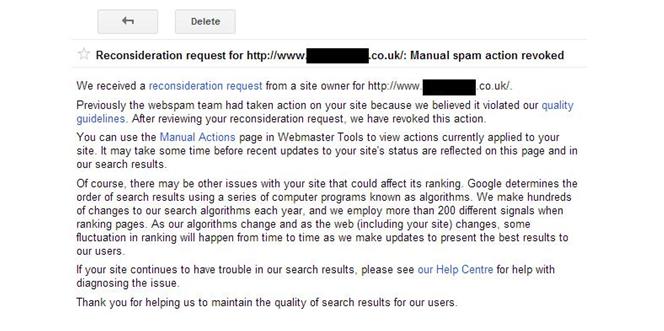
In our experience Google currently takes on average around 8-11 days to respond to requests. So keep monitoring your Google Webmaster Tools after you have sent your reconsideration request and assuming that you have implemented all of our recommendations correctly you should receive a response like this…
If you have any questions about anything in this article, then please leave a comment. If you require assistance managing your link profile or getting a Google penalty removed, then please head to the High Impact contact page or call us directly on +44 (0)1202 237 121.
Author: Julian Saunders is the founder of High Impact.
You can find on him on Google + here.